Supporting traceability in such a highly demanding industry is no longer a matter of best practice. In fact, traceability in the automotive industry is a regulatory requirement ensuring that product quality, safety, and compliance are guaranteed and delivered across the supply chain. Meeting automotive standards and regulations is crucial for manufacturers as it stands as the most reliable way to meet stringent safety requirements, manage the risks, and reduce the dreaded and costly recalls. In this new article, we will explore ISO 26262 and Automotive ASPICE, two global automotive industry standards that have a resounding impact on traceability. What are they? What are their main objectives? How do they shape traceability and more specifically, requirements traceability for automotive manufacturers?
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. The Importance of Traceability in the Automotive World?
2. ISO 26262: Functional Safety and Road Vehicles
- What is ISO 26262?
- Impacts of ISO 26262 on Traceability
- How SodiusWillert’s tools help you comply with ISO 26262?
3. Automotive SPICE (ASPICE)
- What is ASPICE?
-
Impacts of ASPICE on traceability
-
How SodiusWillert’s tools help you comply with ASPICE?
The Importance of Traceability in the Automotive World?
The term traceability refers to the ability to formally identify, trace, and record the source, locations, purposes, and relations between engineering artifacts — throughout the entire lifecycle.
With the increasing number of complex functions and in-vehicle electronics development, manufacturing a car has become a daunting task. Within this paradigm, traceability plays a central role in achieving and strengthening vehicle safety and reliability. Among its numerous benefits, traceability in the automotive industry facilitates manufacturers life by:
- Detecting the slightest defect or quality issues at the earliest stage in the product's development lifecycle.
- Tracing the source and the movements of all parts and components across the supply chain, so that it helps identify bottlenecks and streamline processes.
- Quickly pinpoint the affected vehicles or components in a recall situation, minimizing the risk for users, and reducing the scope and the costs of recall management.
- Ensuring compliance with global safety and quality standards as we are going to see in the next paragraphs.
ISO 26262: Functional Safety and Road Vehicles
What is ISO 26262?
ISO 26262 is an internationally recognized standard that regulates the functional safety of automotive electrical and electronics systems, including hardware and software. It deals with the potential hazards and risks caused by system malfunctions and helps implement the appropriate safety measures.
In more concrete terms, it means that functions such as emergency braking, adaptive cruise control, and similar systems are strictly tested and verified early in the lifecycle in order to prevent and lower the probability of failure. ISO 26262 provides strong guidelines to help these critical systems operate with the maximum amount of reliability and safety.
Adhering to this standard not only contributes to the safety of drivers and passengers but also lays the foundations for car manufacturers to anticipate malfunctions. The ones that result in harmful legal exposure, massive and costly recalls, and reputational damage.
Impacts of ISO 26262 on traceability
The ISO 26262 standard highlights how essential traceability is throughout the entire vehicle safety lifecycle. For this reason, traceability constitutes a central pillar of this international standard and is particularly crucial in the following processes:
- Requirements management
ISO 26262 mandates the end-to-end- traceability of requirements. Requirements traceability refers to the ability to link requirements throughout the entire development process—from the initial conception to design, implementation, testing, validation, and maintenance. This traceable and documented linkage ensures that all requirements are met and verified. It helps involved teams identify impacts from changes and manage potentially associated risks, so that all safety-critical aspects are correctly addressed and verified.
Manufacturers are required to demonstrate that all safety requirements have been addressed, documented, tracked, and validated at every stage of the development project.
- Hazards and risks assessment
ISO 26262 requires meticulous analysis of all possible hazards and associated risks. This specific process of identification and analysis of potential hazards is known as HARA (Hazard Analysis and Risk Assessment). The objective of HARA is to identify and assess potential hazards that could arise in an automotive system due to the malfunctioning behavior of electrical and electronic (E/E) systems. To achieve this, each risk must be linked to an appropriate safety requirement.
The Automotive Safety Integrity Levels (ASIL) is a risk classification scheme defined by ISO 26262, composed of 4 levels (from A to D) based on severity, controllability, and level of exposure. It allows the identification of necessary safety requirements to mitigate the risks associated with potential hazards in the system. Thus, Traceability plays a major role as it ensures that safety requirements are strictly and systematically managed, met, and verified throughout the entire development process.
- Verification and Validation
One of the most critical aspects of ISO 26262 deals with the validation and verification of electronic and software systems. This encompasses verifying whether systems are compliant with safety requirements, as well as testing to make sure that systems are working as intended and safely.
Manufacturers are required to maintain traceable links between all V&V activities, including tests and reviews, and the associated safety requirements. ISO 26262 mandates exhaustive documentation of test plans, cases, and results. This documentation is expected to be traceable from their origins to the safety requirements.
ISO 26262 also pays particular attention to bi-directional traceability. This means that each requirement is traceable in both forward and backward directions.
How SodiusWillert’s tools help you comply with ISO 26262?
One of the most critical aspects of ISO 26262 is ensuring traceability between different artifacts such as requirements, design, implementation, testing, and verification.
SodiusWillert tools like OSLC Connect for Jira, OSLC Connect for PTC Windchill, and other platforms provide seamless connectivity between different engineering tools (e.g., requirements management, systems modeling, test management systems, product lifecycle management, etc.) to enable teams to maintain consistent traceability between all safety-related artifacts.
For example, by linking requirements from IBM DOORS Next to change notices in PLM tools like PTC Windchill, and connecting these with test cases, teams can easily demonstrate compliance with ISO 26262’s demand for traceability across the safety lifecycle.
Automotive SPICE (ASPICE)
What is ASPICE?
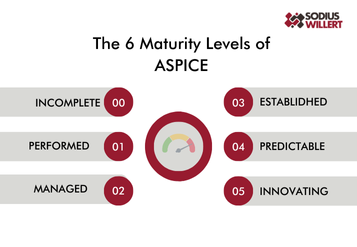
The Automotive version of SPICE (Software Process Improvement and Capability Determination), abbreviated ASPICE, is another fundamental and probably the most current standard of the automotive industry. To be more specific, ASPICE is a maturity model that assesses the maturity of development processes for electronic and software-based systems such as ECUs.
ASPICE provides a framework of 6 levels and is widely used by manufacturers and suppliers to evaluate and improve the quality, performance, and maturity of software within the automotive system. In fact, OEMs usually require ASPICE compliance, which must be demonstrated in regular ASPICE audits.
Impacts of ASPICE on traceability
ASPICE promotes a structured and holistic approach to software development. As a result, traceability plays an essential role in ensuring that software requirements are correctly met, tested, and validated. Manufacturers must ensure that software requirements are correctly traceable to specific elements such as code or test operations.
Now, let's take a closer look at some of the different aspects of requirements traceability in ASPICE.
- Traceability between software requirements and implementation
ASPICE relies on the V-Model, a model demanding that systems requirements be decomposed into software requirements. This mechanism facilitates the creation of traceable links with implementation tasks and ensures that all the requirements are well-addressed during the development phase.
As ISO 26262 did for safety requirements, ASPICE also emphasizes bi-directional traceability. Each software requirement must be traceable to its associated implementation mechanism, as well as the reverse path. This approach helps identify any gaps or inconsistencies and verify if requirements are well-implemented.

The V-model of the systems engineering process (source: Wikipedia)
- End-to-End Traceability
The V-Model, as we already mentioned above, demands a decomposition of requirements (software and systems requirements) and strict evaluation through testing at every stage of development. This meticulous model aims to eliminate many inconsistencies at the earliest stages and helps consolidate end-to-end traceability.
- Change Management and Change Impact Analysis
The ASPICE framework requires that any changes to software requirements, design, or implementations must be systematically tracked, documented, analyzed, and structured to enable, among other things, a thorough analysis of the impact of these changes on the entire system.
How SodiusWillert’s tools help you comply with ASPICE?
SodiusWillert helps automotive manufacturers comply with ASPICE by offering tools that simplify and streamline the development of AUTOSAR-compliant components. With expertise recognized by IBM, our solutions enable engineers with minimal AUTOSAR knowledge to efficiently transform SysML models into AUTOSAR and UML, kickstarting projects without extensive training.
These tools support ASPICE compliance by automating key processes, ensuring adherence to ASPICE maturity level requirements, and providing full traceability from requirements to code. Additionally, our solutions integrate seamlessly with third-party AUTOSAR tools and automate documentation generation, reducing the complexity and effort required for ASPICE audits.
Explore our solutions Solutions for AUTOSAR and ASPICE audits
Conclusion
ISO 26262 and ASPICE are definitely playing a pivotal role in the building of traceability and more specifically, requirements traceability in an era where vehicles rely more than ever on electronics and software.
Shaping a solid and end-to-end traceability strategy, in line with these two major standards, allows automotive businesses to meet their requirements, keep their reputation intact, avoid financial abysses and, most importantly keep drivers safe on the road!

![]()
In addition to ISO 26262, and ASPICE other important automotive standards and regulations contribute to traceability requirements (IATF 16949, ISO 9001, or UN Regulation No. 155.)
Here's an overview of their role:





Leave us your comment